And Glut4 Diabetes
Glut4 Diabetes Exercise Diabetestalk Net
The role of glut4 in insulin resistance is an active area of diabetes research. sugar consumption causes the pancreas to secrete too much insulin. insulin triggers the transport of this protein to the cell surface through a complicated signal transduction mechanism involving the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of proteins and lipids. Insulin and amp-activated protein kinase (ampk) signal pathways are known to be involved in glucose uptake regulation, but the integration of signals between these two pathways in maintaining glucose homeostasis remains mysterious . insulin stimulates glucose uptake into skeletal muscle mainly via the translocation of glucose transporter 4 (glut4) to the plasma membrane . Glucose transporter type 4, also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4, is a protein encoded, in humans, by the slc2a4 gene. glut4 is the insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscle. the first evidence for this distinct glucose transport protein was provided by david james in 1988. the gene that encodes glut4 was cloned and mapped in 1989. at the cell surface, glut4 permits the facilitated diffusion of circulat.
Muscle Groupspecific Regulation Of Glut 4 Glucose
Glut4 Wikipedia
Glut4 wikipedia.
Reciprocity Between Skeletal Muscle Ampk Diabetes
Glut4 content was also unchanged when levels were normalized per wet weight, per total protein, and per dna as an index of cell number. levels of glut4 mrna were similarly not affected by obesity, igt, or niddm whether normalized per rna and glut4 diabetes or for the amount of an unrelated constitutive mrna species. To gain further insight into the mechanisms underlying muscle insulin resistance, the influence of obesity and type 2 diabetes on glut4 immunoreactivity in slow and fast skeletal muscle fibers was studied. through a newly developed, very sensitive method using immunohistochemistry combined with morphometry, glut4 density was found to be significantly higher in slow compared with fast fibers in. Glucose transporter 4 (glut4) and diabetes 1. liu lz, cheung sc, lan ll, ho sk, chan jc, tong pc. the pivotal role of protein kinase c zeta (pkczeta) in insulin2. braiman l, alt a, kuroki t, ohba m, bak a, tennenbaum t, et al. activation of protein kinase c zeta induces serine 3. tan sx, ng. Impaired insulin action in diabetes, as well as disorders of glut4 vesicle trafficking in the muscle, are involved in defects in insulin-stimulated glut4 translocation. since the rab gtpases are.
The impact of diabetes and insulin therapy on glut 4 expression also varied as a function of muscle group. after four weeks of diabetes, glut 4 levels were reduced by approximately 50% in cardiac muscle, soleus, and gastrocnemius. in contrast, glut 4 content in rectus abdominis and vastus lateralis was similar to that in control rats. The effect of intensive insulin therapy on the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (glut4) expression in skeletal muscle in type 1 diabetes studies in normal man and rodents have demonstrated that the expression of the dominant glucose transporter in skeletal muscle, glut4, is regulated by insulin at supraphysiological circulating levels. Type 2 diabetes has genetic and environmental factors that increase the chances of an individual of getting it. among the environmental factors are high cholesterol and obesity, and among the genetic factors are genes involved in glucose metabolism or glucose intake signaling such as glut4. Exercise, glut4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake glucose is an important fuel for contracting muscle, and normal glucose metabolism is vital for health. glucose enters the muscle cell via facilitated diffusion through the glut4 glucose transporter which translocates from intracellular storage depots to the plasma m.
Glut4 is reduced in slow muscle fibers of type 2 diabetic patients. is insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes a slow, type 1 fiber disease? to gain further insight into the mechanisms underlying muscle insulin resistance, the influence of obesity and type 2 diabetes on glut4 immunoreactivity in slow and fast skeletal muscle fibers was studied. Glut4 (slc2a4) is the insulin-responding glucose transporter, found predominantly in muscle cells and adipocytes (fat cells). after a meal, glucose that is absorbed from the digestive system and circulates in the blood now stimulates the release of insulin from the pancreas (figure 4. 10). this insulin is the signal for a rapid transfer of glut4 and glut4 diabetes in muscle and adipose cells to the cell membranes. Indicate that,although there is some overlap of glut4 with markers of the endocytic system such as the tfr,a tissue,and is severely disrupted in type ii diabetes 1 (box 1); second,disruption of glut4 expression in mice results in insulin resistance 4; and overexpression of glut4 ameliorates diabetes in the db/db mousemodel5.
High insulin and high glucose-induced glut4 degradation is regulated by ubiquitin-proteasome dependent pathway chronic exposure (18 h) of iso chronic exposure (18 h) of isolated rat adipocytes to high insulin, 100 nm, and high glucose, 25 mm, (hi/hg) causes insulin resistance characterized by decreased sensitivity and maximal responsiveness of glucose uptake. Glut4 in muscle and adipose tissue is indispensable for glucose homeostasis. 349 specific deletion of glut4 from muscle or adipocytes dysregulates glucose homeostasis and promotes insulin resistance to a much greater extent than deletion of insulin-signaling components from these tissues alone. 350 muscle-specific glut4–knockout (mg4ko) mice develop hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance by 8 weeks of age.
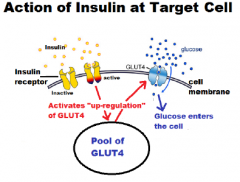
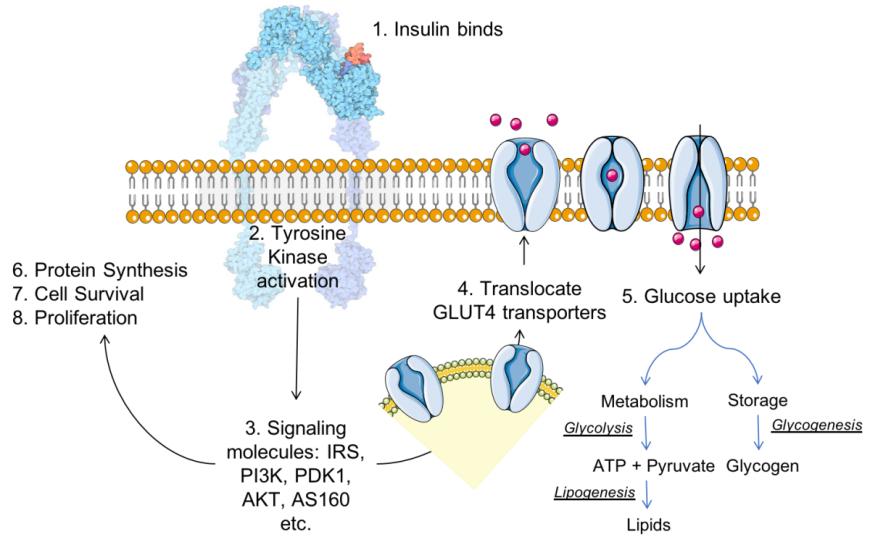
The mechanism for glut4 is an example of a cascade effect, where binding of a ligand to a membrane receptor amplifies the signal and causes a cellular response. in this case, insulin binds to the insulin receptor in its dimeric form and activates the receptor's tyrosine-kinase domain. the receptor then recruits insulin receptor substrate, or irs-1, which binds the enzyme pi-3 kinase. Glut4 is in the family of solute carriers and is responsible for facilitating the transport glucose into the cells in response to insulin. for this reason, mutations in glut4 have been associated with type 2 diabetes. the glut4 gene has been mapped to the region 13 in the short arm of chromosome 17 (17p13). F and g: confocal imaging of glut4 and plasma membrane marker caveolin-3 (cav3) was performed on clamped (insulin-stimulated) gastrocnemius cryosections. quantification of sarcolemmal glut4 was performed by imagej. n = 11–15/group. h: vastus lateralis homogenates were applied to a 4–12% sds-page. western blotting was performed for hkii and.
Glut4 has long been known to be an insulin responsive glucose transporter. regulation of glut4 has been a major focus of research on the cause and prevention of type 2 diabetes. understanding how insulin signaling alters the intracellular trafficking of glut4 as well as understanding the fate of glucose transported into the cell by glut4 will be critically important for seeking solutions to. The primary regulatory mechanism by which glucose uptake takes place is via insulin-stimulated transport of glucose into skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, primarily mediated by glucose transporter protein type-4 (glut4). glut4 is a key component in glucose homeostasis and the removal of glucose from circulation.
Apr 23, 2018 · total glut4 content in skeletal muscle from individuals with type 2 diabetes is normal; however, recent studies have demonstrated that translocation of glut4 to the plasma membrane is decreased in response to insulin stimulation. In contrast, in type 2 diabetic subjects, glut4 density was significantly lower in slow compared with fast fibers. glut4 density in slow fibers from diabetic patients was reduced by 9% compared with the weight-matched obese subjects and by 18% compared with the lean control group.
The present study and glut4 diabetes was designed to determine whether intensified insulin replacement therapy for 24 h given to patients with type 1 diabetes in poor metabolic control was associated with an adaptive regulation of glut4 mrna and protein levels in vastus lateralis muscle. Total glut4 content in skeletal muscle from individuals with type 2 diabetes is normal; however, recent studies have demonstrated that translocation of glut4 to the plasma membrane is decreased in response to insulin stimulation.
Komentar
Posting Komentar